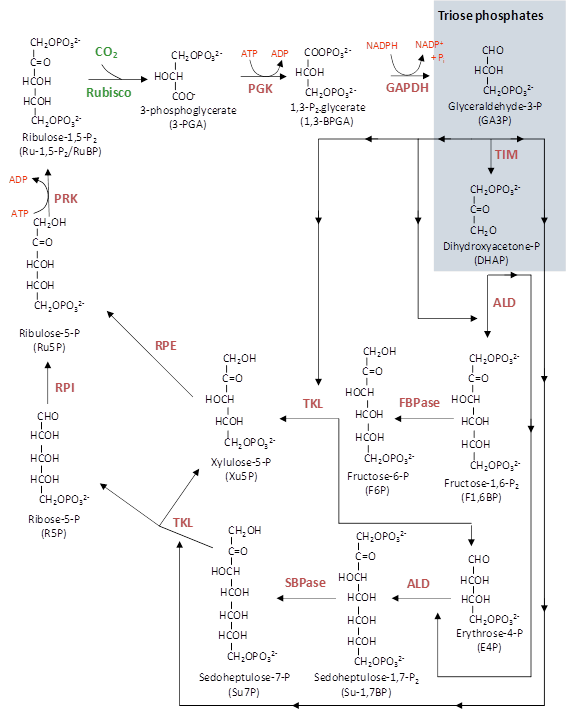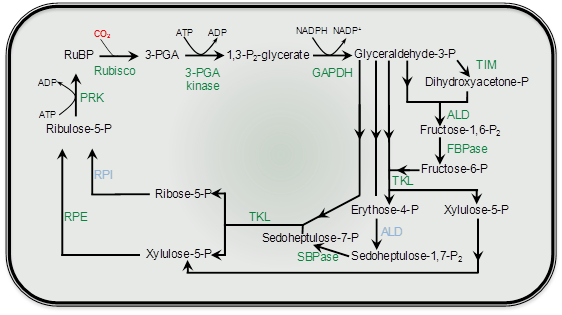
Figure 2.2. A simplified (above) and detailed (below) description of the photosynthetic carbon reduction (PCR) cycle. The fixation of CO2 by Rubisco to the acceptor molecule RuBP initiates the cycle with the production of two molecules of PGA. The subsequent, enzyme catalysed, generation of cycle intermediates are cycled to either regenerate RuBP or produce triose phosphates which are precursors for carbohydrate synthesis. The cycle is powered by the co-factors NADPH and ATP that are synthesised from the chloroplast electron transport chain. Enzymes include: PGK, phosphoglycerate kinase; GAPDH, glycraldehyde-3- phosphate dehydrogenase; TIM, triose phoshphate isomerase; ALD, aldolase; FBPase, fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase; TKL, transketolase, SBPase, seduheptulose-1,7-bisphosphatase; RPI, ribose-5-phosphate isomerase; RPE, ribose-5-phosphate epimerase and PRK, phosphoribulose kinase. (Courtesy Robert Sharwood).